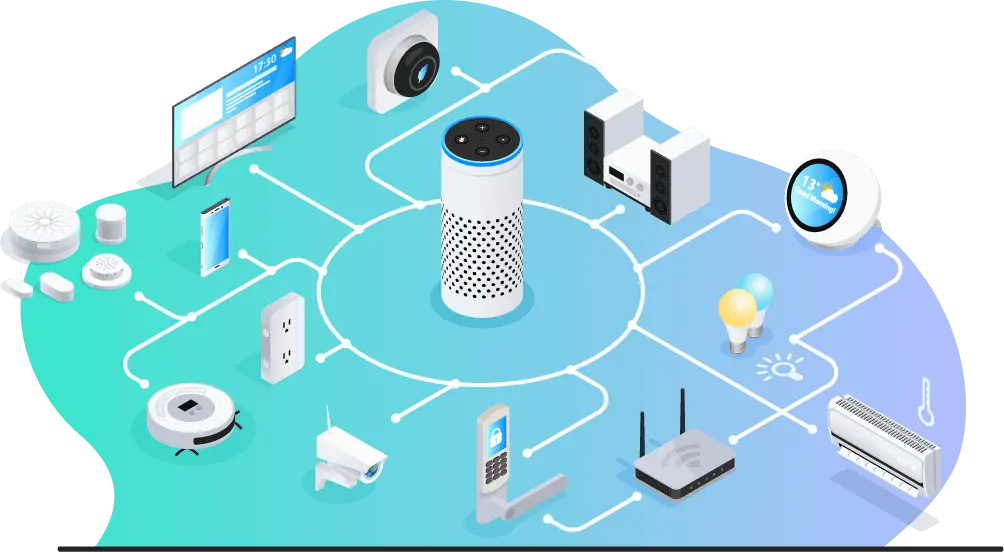
Image what you will get when integrate multi-room streaming amplifier into your home automation.
What is Home Automation?
Home automation uses schedules, rules, and scenes to trigger smart devices to do things for us.
Schedules make something happen at a fixed time; for example, your living room speaker turn on at 7:30 a.m. every weekday morning in the summer.
Rules make your devices respond to specific actions; for example, your kitchen speakers turn on only when someone is in the kitchen.
Scenes group devices so each performs a specific action when triggered. Your blinds raise, for example, and your Google Nest Mini reads your calendar when you wake up in the morning.
System Component of Home Automation
Home automation has three main components that work together: a hub, a network, and devices. Very basically they work like this:
- The hub gives the commands.For example, to have music in your living room at 7:30 every summer morning, you would first program your hub. This could be an Amazon Echo Show. It could also be a local (non-cloud-based) option like Home Assistant, or just your smartphone with an automation app such as IFTTT.
- The network communicates the commands over Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee/Z-Wave, and now Thread.
- Smart devices receive the commands and carry them out.
Your hub would then send the command over Wi-Fi, Zigbee, or Thread. And, finally, your smart bulb (with a motion sensor) would receive the message and flip on the lights for you automatically.
Here are some common hubs with the network technologies they use, including a few alternatives that favor local automations.
| Hub | Wi-Fi | Zigbee | Z-Wave | Thread |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nest Hub (2nd Gen) | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| Amazon Echo 4th Gen | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Home Assistant | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Hubitat Elevation | Limited | Yes | Yes | No |
| SmartThings Hub v3 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Vivint Smart Hub | Yes | No | Yes | No |
Understand Your Network
The most typical network set-up for automated homes is hybrid. Low-power devices like smart bulbs and motion sensors communicate locally with Bluetooth, Zigbee, or Z-Wave, then with the Cloud via your Wi-Fi connection. Here’s a quick breakdown of the ways hubs communicate with our devices.
- Wi-Fi.When you use Wi-Fi, your IoT devices use your internet connection. While this is convenient, it’s also resource-heavy and can crowd your network resulting in slower speeds, especially if you have a lot of different IoT devices running at once.
- Bluetooth:Bluetooth is a lighter, mesh technology that lets you control and monitor IoT devices and automate systems without Wi-FI.
- Z-Wave:Z-Wave is another wireless technology that won’t interfere with your Wi-Fi, operating, instead, on a low-power 908.42 Mhz frequency in the U.S. and Canada.
- Zigbee:Similar to Z-Wave, ZigBee is a mesh network and universal language that lets IoT devices communicate.
Multi-room Streaming Amplifier in Home Automation

All multi-room streaming amplifier from OpenAudio Support WiFi and Bluetooth, both audio and non-audio data.
There are two typical ways you can integrate HOLOWHAS series devices (HOLOWHAS, HOLOWHAS Ultra, HOLOWHAS Plus, HOLOWHAS Max, HOLOWHAS Ultra-GC, HOLOWHAS Plus-GC and AVR-16200) into your home automation: first, use Alexa with Amazon Echo and use WebAPI with Home Assistant.